CARLY CASSELLA
10 MAY 2019
An extremely sick teen with a superbug an infection proof in opposition to antibiotics has had her life saved by an ingenious therapy designed accurate for her.
Setting up a cocktail of bacteria-hungry viruses, genetically engineered to hunt at their easiest, an world team of physicians and microbiologists delight in no longer totally prolonged a life, they delight in got completed a scientific first, bringing attention to a therapy long-left out in the West.
Recognized with cystic fibrosis as quite of one, Isabelle Carnell-Holdaway, now 17, has struggled with an on-again, off-again superbug an infection since age 8.
At some stage in her childhood, the Mycobacterium abscessus an infection – connected to tuberculosis and leprosy – was kept at bay, nevertheless a few years ago, after present process a double lung transplant, all of it came abet with a vengeance.
Impervious to the well being center’s antibiotics, Carnell-Holdaway’s liver and lungs soon began to fail, and her probabilities of survival snappy slipped below one p.c. In a final ditch strive, her mother urged something unconventional: what about phage therapy?
Bacteriophages are viruses named and renowned for their potential to luxuriate in superbugs love the one plaguing Carnell-Holdaway, regardless that beneath no circumstances particularly that one.
Chanced on in the gradual 1800s, they delight in got been extinct for over a hundred years in the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe, successfully treating an total diversity of bacterial infections, along side dysentery, tuberculosis, salmonella, E. coli, and staph.
In one Polish paper, where antibiotics had been ineffective for practically all 550 sufferers, phage therapy if truth be told labored for over 90 p.c.
Carnell-Holdaway’s mother wished to know if something an analogous would perchance be executed for her daughter, nevertheless in the UK, the experimental therapy remains controversial and understudied.
Apart from the success of antibiotics, one amongst the explanations the West has largely left out these hopeful outcomes is that many stories, along side the one talked about above, attain no longer embody control groups. The compare also tends to be written in languages as antagonistic to English.
“Isabelle’s fogeys knew we had been making an try to work on this phage therapy, so when the time came that we had no other frail therapies to make use of and ongoing indicators of an infection – they had been desperate for other alternatives,” senior creator and doctor Helen Spencer informed The Honest.
There was every reason to substantiate out, especially since doctors in San Diego had no longer too long ago extinct phages to successfully treat a human multidrug-resistant bacterium known as Acinetobacter baumannii.
The University of Pittsburgh is home to the sector’s greatest collection of bacteriophages, so it gave the influence love a accurate kind characteristic to delivery out. The curator of this 15,000-vial collection, microbiologist Graham Hatfull, was nervous nevertheless more than joyful to oblige. And so, his team spent months buying for the applicable phages to consume on Carnell-Holdaway’s an infection.
Whittling thru the contenders, Hatfull landed on three viruses in explicit. One virus, named “Muddy” came from a rotting eggplant and so it was a natural born killer. The opposite two, named ZoeJ and BPs, wished quite of more encouragement.
In actuality, this sleepy behaviour is one amongst the components defending phage therapy abet. Rather a few these viruses accurate need to no longer lethal ample to be effective as treatments, and when their differ is so explicit, they became all nevertheless needless.
“I had a sense that this collection was greatly extremely effective for addressing all styles of questions in biology,” Hatfull says. “But we didn’t think we would ever derive to a couple extent of the use of these phages therapeutically.”
The principle could be very of genetic tweaking. In this case, ZoeJ and Bps had one gene removed in explicit, which makes them curl up and tumble asleep after they enter a bacterial cell. With out this restful burden, the phages had been now no longer so merciful, replicating many times till their offspring at final burst from the host cell and destroyed it.
“Antibiotics are very effective, nevertheless they’re a blunt instrument,” Hatfull informed The Honest.
“With phages or no longer it’s the reverse stop of the spectrum. They’re very explicit, or no longer it is a centered strike, that you just have to to no longer going to thrill in an impact on the comfort of the microbiome and in addition they’re low toxicity, on fable of they intention no longer infect human cells.”
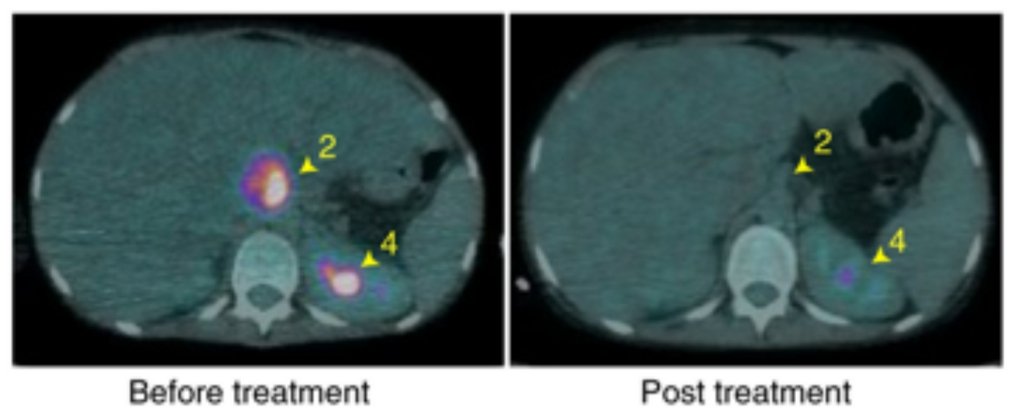
After purifying the phages, security-sorting out them and mixing them as a lot as derive a stronger front, the recent remedy was ready. In June of 2018, Carnell-Holdaway was given an IV twice on a typical basis of this viral cocktail, containing a thousand million phage particles in every dose.
Six weeks later, the an infection had all nevertheless disappeared from her liver, and this day, totally one or two pores and skin nodules dwell.
While the patient hasn’t been cured of the superbug an infection entirely, she has resumed all trendy activities and the bacteria has shown no resistance to the therapy thus a ways. Moreover, although they attain, researchers will soon be ready so as to add a fourth phage to the mix.
“Here is de facto a historical moment,” Steffanie Strathdee, the phage expert and doctor who labored on the earlier compare in San Diego, informed NPR.
“Here is the first time that a genetically engineered phage has been extinct to successfully treat a superbug an infection in a human being,” Strathdee says. “It is terribly racy.”
Within the published case view, the authors argue that faced with rising antibiotic resistance, searching extra into genetically-modified phage therapy would perchance be in a characteristic to set critical more lives.
“Phage therapy appears to be [the] most promising quite loads of to antibiotics that’s on the scene,” Strathdee added.
This view has been published in Nature Remedy.




Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.