In phrases of organ transplant surgical operation, doctors are racing in opposition to the clock — and time is no longer on their facet.
A team of clinicians must first put off the organ from its donor, gadgets of gloved palms coordinating to deftly gash tissue from the body. Doctors then prep the harvested organ for transport to its recipient, who will be hours away by airplane. Once the organ reaches its destination, the transplant operation can lastly begin; again, surgeons must work impulsively to be particular both the affected person’s security and the organ’s viability.
This description can also save organ transplant surgical operation sound love a TV drama, with scientific personnel sprinting thru clinic corridors carrying coolers packed with body elements. However the full rushing about raises a inquire that is powerful more essential than a TV tag: How long can an organ final exterior the body and live fit for transplantation?
It is depending on the organ. For now, the time window will be between 4 and 36 hours. However at some point, doctors hope as a method to shield organs for weeks on cessation.
Associated: 12 Fantastic Pictures in Remedy
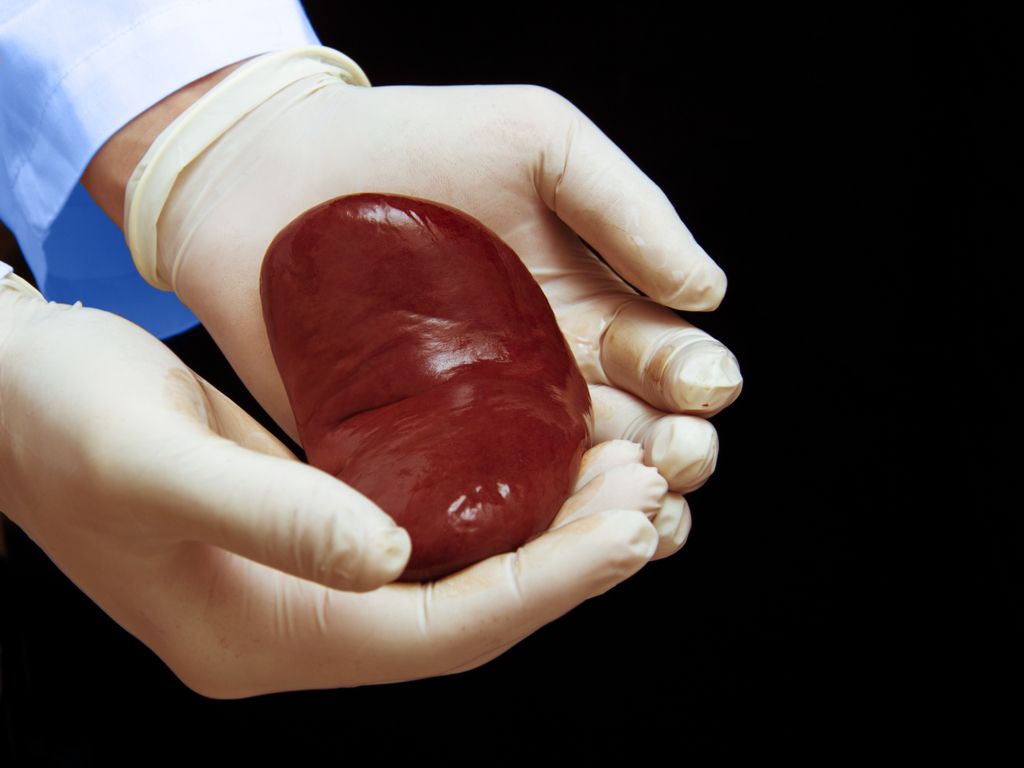
Organs on ice
In 2018, more than 36,500 organ transplants took articulate within the U.S. on my own, primarily primarily based on the United Community for Organ Sharing (UNOS). By far, kidneys were the most steadily transplanted organ, with more than 21,000 transplants taking articulate final one year. The following most steadily transplanted organs were the liver, coronary heart and lung, in that portray, adopted by pancreas, gut and multiorgan transplantations.
Most organs are placed in “static cold storage” after they’re harvested, meaning that the organ is deposited in a cooler stuffed with ice, primarily primarily based on a 2019 yarn within the Journal of Global Scientific Learn.
“The fresh thought for cold preservation is extremely powerful love after we attach our food within the fridge,” said Dr. Mingyao Liu, the director of the Institute of Scientific science and a professor of surgical operation, medicine and physiology at the College of Toronto.
Sooner than inserting an organ in cold storage, doctors first flush the tissue with a “preservation acknowledge” to shield the organ from injury attributable to the intense cold, Liu knowledgeable Dwell science.
At body temperature, cells pump chemicals inner and exterior of their membranes in portray to shield low concentrations of sodium and excessive concentrations of potassium inner the cell. However cells which will seemingly be cold can not pump effectively. Chemicals leak across their membranes, and over time, the leaky cells swell up with extra fluid, sustaining essential injury. Preservation solutions attend extend this injury by conserving sodium and potassium stages in test. These solutions can moreover hold nutrients and antioxidants to shield the cells and subdue irritation, Liu said. In combination with ice and a cooler, preservation solutions can shield organs viable for hours after harvest.
At temperatures between 32 and 39 levels Fahrenheit (0 and 4 levels Celsius), cell metabolism falls to about 5% of its accepted rate, so tissues burn thru their vitality stores far more slowly and require less oxygen to shield their process. On yarn of this, cooling an organ helps extend the onset of ischemia, a condition by which tissue becomes damaged or dysfunctional attributable to a scarcity of oxygen.
Striking an organ on ice moreover stretches its cells’ restricted vitality stores, struggling with unpleasant metabolites from constructing up and breaking down the organ’s tissues, primarily primarily based on a 2018 yarn in the Yale Journal of Biology and Remedy.
Amongst steadily transplanted organs, hearts lose viability the quickest when kept in a cooler, said Dr. Brian Lima, the director of coronary heart transplantation surgical operation at North Shore College Scientific institution in Manhasset, Recent York. Ideally, a coronary heart is just not placed in static cold storage for more than 4 to 6 hours, he said. On the 4-hour mark, coronary heart cell goal begins to fail and the probability that the organ will malfunction in its recipient rises dramatically. Transplant organ failure, known as essential graft dysfunction, is the “most feared complication” linked with steady organ transplants, Lima said.
“The coronary heart … is most sensitive to lack of blood float,” Lima said. “The kidneys, on the rather hundreds of hand, are very resilient.” Harvested kidneys can live viable for 24 to 36 hours in cold storage, longer than any of the rather hundreds of high-four transplant organs. Lungs can live viable for 6 to eight hours, Lima said, and the liver can live in cold storage for roughly 12 hours, primarily primarily based on Dr. James Markmann, head of the Division of Transplantation at Massachusetts Long-established Scientific institution in Boston.
Associated: High 10 Fantastic Facts About Your Coronary heart
An alternate manner
Though low tech, the ice cooler manner “gives a straightforward and efficient solution to attend and transport organs” and has been widely weak since the 1960s, primarily primarily based on the 2018 yarn by Liu. However the technique is no longer without its drawbacks. No longer simplest attain organs in cold storage lose viability inner hours, but moreover, doctors save no longer hold any solution to evaluate the usual of the chilled organs, Liu said.
In overall, no goal test can expose clinicians if an organ is clean purposeful when the organ in inquire sits in a frigid cooler, its cell metabolism winding down in gradual walk. On the opposite hand, one change to cold storage does allow doctors to test on organs ahead of they’re transplanted, and this selection can also soon become more accepted, consultants knowledgeable Dwell science.
This alternate preservation manner, known as perfusion, involves hooking up a harvested organ to a machine that pumps oxygen- and nutrient-rich fluid thru the organ’s tissues, as the coronary heart would attain within the body, primarily primarily based on the 2018 yarn from the Yale journal. Whereas plugged into the machine, as the organ metabolizes vitality and produces raze, its sugar stores are replenished and its toxic metabolites cleared away.
Sooner than surgeons harvest an organ, the donor’s coronary heart stops pumping oxygenated blood to the tissue for a period of time, which causes injury. Placing an organ in a perfusion machine can also give the tissue a giant gamble to increase, Markmann said. As well to, clinicians can test in on the organ by monitoring stages of the metabolite lactate circulating within the procedure, he said. Cells utilize lactate one day of accepted metabolic solutions, so “if the organ is working properly, the lactate wants to be cleared” over time, Markmann said.
“Lactate is at simplest a inaccurate metabolic measure of perfusion thru the body,” nonetheless it clean serves as a superior measure compared with eyeballing a advance-frozen organ ahead of transplantation, Lima added. Looking on the organ, doctors can moreover assess the properly being of the tissue by rather hundreds of measurements, a lot like the manufacturing of bile by the liver.
Associated: 27 Oddest Scientific Situations
May maybe per chance perfusion shield organs wholesome for longer?
Some perfusion systems clean require that the organ be cooled down as phase of the preservation process, but inner the final 20 years, various review groups hold opted to shield the organ warm and flood the tissues with warm blood. At temperatures between 68 and 92 F (20 and33 C), isolated organs goal powerful as they attain within the human body. Each and every hot and cold perfusion systems are now widely weak in Australia and the U.Ok., but most of these gadgets live in scientific trials within the U.S.
On the opposite hand, one perfusion procedure within the U.S. made headlines in December as phase of a significant-of-its-kind coronary heart transplantation. Doctors at Duke College Scientific Heart in Durham, North Carolina, eliminated a affected person’s coronary heart after it had stopped beating; they then of route “reanimated” the organ the utilization of a warm perfusion procedure, CNN reported. Generally, hearts are eliminated from mind-useless donors ahead of the organ stops beating, to steer particular of in depth injury from ischemia. Doctors previously “reanimated” pediatric hearts within the U.S., but they’d never weak the procedure on an adult organ. In worldwide locations which hold weak the procedure for years, the donor pool of acceptable hearts has expanded by about 30% to 40%, Lima said.
“If that interprets into the US, we’re talking about big, big numbers,” he added.
Dr. Jacob Schroder, a Duke College assistant professor of surgical operation and one in every of the surgeons who helped save the landmark coronary heart transplant, knowledgeable CNN that the utilization of the procedure nationwide could maybe “save bigger the donor pool and option of [heart] transplants by 30%.”
Though the donor pool can also save bigger, would the condition of the organs give a boost to? As of yet, few stories hold straight compared cooler storage to perfusion, but anecdotally, perfused organs usually appear to fare better.
As an instance, in a single trial evaluating a liver perfusion procedure to accepted cold storage, doctors rejected simplest 16 perfused livers, compared with 32 that came from coolers, and the perfused organs looked less damaged, primarily primarily based on Stat Info. Liu said that he’s seen the same trends in his delight in work with lung transplants. Liu and his colleagues developed an “ex vivo perfusion procedure” for lungs; ahead of its introduction, fewer than 20% of donor lungs were successfully transplanted at his university’s clinic. Now, this procedure has expanded its process by 70%, “with fantastic outcomes,” primarily primarily based on a 2018 yarn.
Generally, lungs live curved up to the perfusion procedure for 4 to 6 hours, but experimental work with animal organs means that perfused lungs could maybe live viable for 12 to 18, and even per chance up to 36 hours, Liu said. He added that, at some point, an organ will be perfused for weeks. The longer that organs will be left on the procedure, the more time clinicians would prefer to restore damaged tissue. Liu and his colleagues are now investigating how irritation and cell death will be inhibited in perfused lungs. However within the future, per chance organs will be handled with gene or stem cell therapies whereas curved to a perfusion machine, he said.
For now, on the change hand, most donated organs clean plug to their recipients nestled in coolers of melting ice. Why?
“Rather of route, the hurdle with [perfusion] is the price,” Lima said. A perfusion procedure for a single organ can stamp various thousand greenbacks, which obviously surpasses the price of a mature cooler, he said. As few stories hold compared perfusion to accepted cold storage, no “earth-shattering files” exist that would maybe persuade hospitals to save various the swap nationwide.
However given the unusual success of the Duke coronary heart transplant, Lima said that perfusion can also soon become the accepted of care.
- 9 Recent Suggestions to Select Your Coronary heart Wholesome
- High 10 Ineffective Limbs (and Other Vestigial Organs)
- 7 Scientific Myths Even Doctors Assume
Originally published on Dwell science.




Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.