Cooling, or aircon, is extra complicated than heating. Per the US Division of Energy, heating and cooling systems emit over a half of billion a entire bunch carbon dioxide into the atmosphere each 365 days. Moreover, most of our structures manufactured from the concrete, whose manufacturing is a foremost offer of carbon emissions. And as soon as it’s completed, heating and cooling structures change into a foremost energy sink.
One ethical manner to decrease the amount of cooling a constructing wants is to be obvious it shows away infrared radiation. Passive radiative cooling supplies are engineered to rupture this extremely effectively.
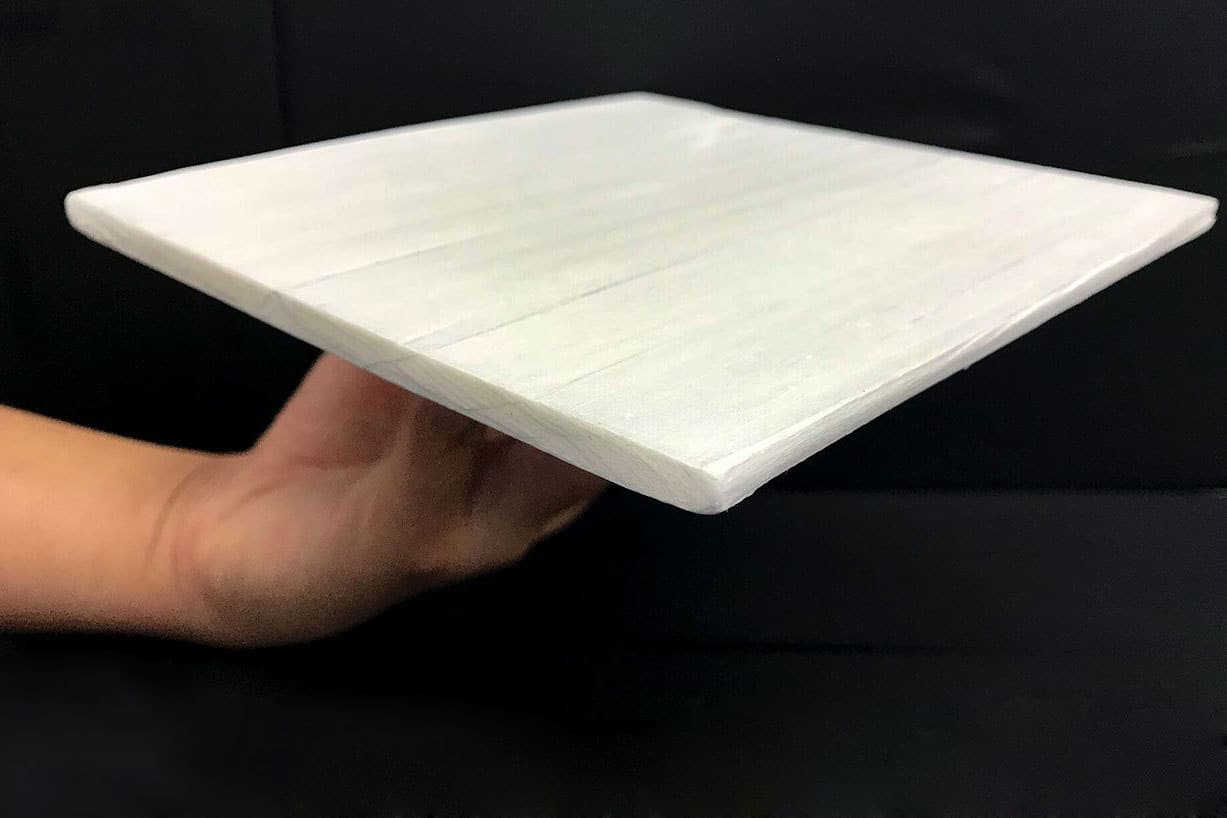
Now, a current assemble of wood that radiates heat into home might well offer some reduction. The fabric, if dilapidated on a constructing’s exterior, might well drop a constructing’s temperature as great as 10°C and decrease cooling costs as great as 35%.
Liangbing Hu, a supplies scientist on the College of Maryland and his colleagues created this fabric by eradicating the ‘lignin’ from natural wood the utilization of hydrogen peroxide.
Well presumably, the homes manufactured from excessive-tech wood might well abet us stop cool and furthermore decrease carbon emissions by reducing energy dilapidated on aircon.
High-tech cooling wood
Lignin is a part of the cell partitions in trees, that acts as a glue retaining the straw strands collectively. Lignin is a stable emitter of IR light.
The team eliminated this from the wood by merely soaking the basswood in a solution of hydrogen peroxide, which chops in most cases long lignin molecules into tiny fragments. The fragments diffuse out of the solution and might well also be washed away. The team then dilapidated a sizzling press, an industrial vise for making wood composites, to compress the rest cellulose and hemicellulose parts collectively. The tip result used to be an engineered wood with eight cases the energy of natural wood.
To boot to, the cellulose within the wood shows visible light and most interesting absorbs very low stages of near-infrared light. It merely methodology the cooling wood shows a couple of the parts of sunlight correct abet to the ambiance.
As a result, a constructing constituted of this fabric would transmit barely any heat indoors. The team furthermore chanced on that the fabric can accumulate heat produced indoors, which is emitted at a clear wavelength differ to sunlight. In some unspecified time in the future of cooler nights, the wood helps unlock the warmth outdoors, making it helpful day and night.
It might most likely well decrease aircon costs:
If this fabric were applied to the outsides of structures within the warm climates, the passive cooling assemble might well decrease aircon costs by as great as 35%, the researchers reported within the journal science.
Hu says the cooling wood is awfully dense and has a tensile energy of around 404 megapascals, making it 8.7 cases stronger than natural wood and similar to metal structure supplies at the side of steel.
But, because the cooling wood prohibit the warmth from the sun from getting indoors, so it might per chance possibly well add extra heating costs at some stage in chilly weather. Hence, Hu says the fabric is handiest suited for warm areas with long summers and quick winters.
This multifunctional, scalable cooling-wood fabric holds promise for future energy-efficient and sustainable constructing applications, enabling a wide reduction in carbon emission and energy consumption.




Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.