(CNN)There is a “original beast” lurking on the market in the universe.
It first showed itself four years ago, when astronomers seen a shimmering burst of light coming from a tiny galaxy about 500 million light-years from Earth.
Now, they’re mindful about it used to be a mercurial blue optical transient, captured in radio waves and X-rays. It produced one in every of the fastest outflows ever seen, blasting out gasoline and particles at higher than 55% the payment of light.
The amount of subject topic in the 2016 explosion used to be between one to 10% of the mass of our sun, and it represents a original form of explosion in the universe, in accordance to a undercover agent revealed Tuesday in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
These mercurial blue optical transients, or FBOTs, are not easy to recall. They’re rapid, energetic and highly efficient explosions that recede away swiftly.
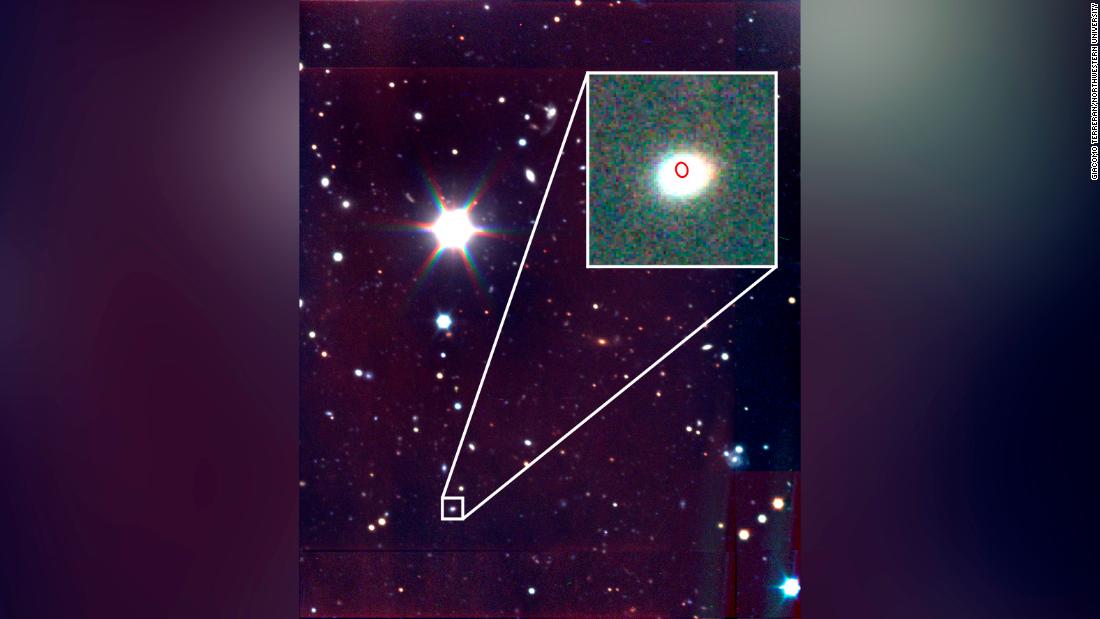
Handiest three enjoy been seen to since they were identified in 2014, including this original one identified as CSS161010. The explosions are so sizzling that they give off a blue glow. Their ephemeral glow and fading course of is blueprint sooner than a supernova, an additional and extra shimmering star that explodes and ejects most of its mass sooner than dying.
Essentially the most successfully-identified of those three events belongs to AT2018COW, or “The Cow,” a rare tournament detected in 2018 that used to be doubtless the beginning of a sunless hole or neutron star. However the 2016 tournament used to be brighter, sooner and heavier.
“We notion we knew what produced the fastest outflows in nature,” said Raffaella Margutti, senior undercover agent author, assistant professor of physics and astronomy in Northwestern University’s Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences, in a assertion.
“We notion there enjoy been entirely two systems to produce them — by collapsing a large star with a gamma ray burst or two neutron stars merging,” said Margutti, who can also be a member of Northwestern’s Heart for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Research in Astrophysics.
“With this undercover agent, we’re introducing a third methodology to originate these outflows. There is a original beast on the market, and or not it’s ready to produce the the same energetic phenomenon.”
Margutti and her colleagues adopted up on 2016 observations of the explosion made one by one by researchers on the Catalina Actual-time Transient Look for and the All Sky Computerized Look for for Supernovae. These practice-united statesin X-rays and radio waves utilized the Keck Observatory telescopes on Maunakea in Hawaii, the arena’s largest optical and infrared telescopes.
“We seen system defects in reasonably about a galaxies that we couldn’t trace,” Margutti said. “However we couldn’t come by data beginning air the optical wavelength, so we couldn’t undercover agent them extra. We would honest name them ‘queer supernovae.’
“The optical wavelengths can uncover us in regards to the particles appealing slowly in an explosion. However ‘appealing slowly’ is peaceful 10,000 kilometers per 2nd. When you happen to would cast off to undercover agent the sooner particles, then you definately would possibly perhaps additionally simply need to make employ of X-rays and radio waves. Then you definately would possibly perhaps additionally save all of them collectively to undercover agent a extra complete picture.”
This FBOT fled the scene too swiftly for astronomers to search out out what in actuality brought about it, however they can come by knowledgeable guesses per what they be taught about all these explosions.
“The Cow and CSS161010 were very reasonably about a in how mercurial they were ready to breeze up these outflows,” Margutti said. “However they arrive by share one component — this presence of a sunless hole or neutron star internal. That is the most necessary ingredient.”
The sunless hole or neutron star is helping to power the explosion of topic, or outflow, of the burst.
One of many reasonably about a inviting things about this explosion is where it occurred, in a dwarf galaxy come the Eridanus constellation. Whereas our massive Milky Potential galaxy accommodates billions of stars, this tiny galaxy entirely has about 10 million.
This aligns with the old FBOTs, which also occurred in diminutive galaxies, which would possibly additionally very successfully be residence to the explosions because they enjoy much less metals than reasonably about a galaxies.
“Every time a superstar dies or neutron stars merge, they give metals lend a hand to the environment,” said Giacomo Terreran, a postdoctoral associate at Northwestern’s Heart for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Research in Astrophysics who took the Keck observations.
“Little galaxies enjoy a tiny amount of metals because not many stars enjoy died there,” Terreran said. “This has an influence on how reasonably about a stars are living their lives. We deem that or not it’s not by likelihood that we entirely acquire these very rare transients in these tiny galaxies.”
The FBOTs, especially this detection which produced an optical explosion, X-rays and radio waves, provides astronomers with unfamiliar data in regards to the universe.
“The major discovery is the finding of a original form of explosion in the universe that’s ready to produce relativistic outflows that elevate a broad amount of vitality,” Margutti truly helpful CNN. “[FBOTs tell us] that the unknown is peaceful very grand there, and in actuality in the lend a hand of the corner — that there exists queer systems stars can die, and with fireworks.”
Previously, entirely gamma ray bursts were notion to enjoy this form of energetic output. However these detections of FBOTs uncover astronomers that whatever mechanism of jet is launching in gamma ray bursts happens equally in an fully reasonably about a draw, Margutti said.
“We know that the star that’s enthusiastic right here is highly reasonably about a from those who produce [gamma ray bursts], and that the environment around CSS161010 has grand higher density than in [gamma ray bursts],” Margutti said.
Apt now, the final notice cause in the lend a hand of the set aside off in the lend a hand of this FBOT is that “a queer direction of [star] evolution ends in a stellar explosion,” Margutti said. No topic is left in the lend a hand of by that explosion, whether it be a sunless hole or neutron star, powers the FBOT.
The researchers said they cannot rule out that right here is potentially a superstar being disrupted by a medium-sized sunless hole, however they favor the broad star explosion scenario.
Now, the researchers need to know why these happen, meaning finding extra FBOTs.
“The next step after finding that one thing does exist is to cherish why it is so rare,” Margutti said. “The major’s to search out this rare form of transient among the many hundreds and hundreds of explosions at evening.”




Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.