For the reason that 1980s, researchers were running experiments making an strive to acquire particles that invent up shadowy topic, an invisible substance that permeates our galaxy and universe. Coined shadowy topic because it affords off no gentle, this substance, which constitutes extra than 80 percent of topic in our universe, has been proven over and over to persuade fashioned topic via its gravity. Scientists comprehend it is some distance available nonetheless enact no longer know what it is some distance.
So researchers at Caltech, led by Kathryn Zurek, a professor of theoretical physics, maintain long gone lend a hand to the scheme starting stage to maintain in mind most up-to-date suggestions. They’ve been taking a seek for into the probability that shadowy topic is made up of “hidden sector” particles, which can perhaps perhaps be lighter than particles proposed previously, and can, in theory, be stumbled on the utilization of tiny, underground table-top devices. In distinction, scientists are making an strive to acquire heavier shadowy topic candidates known as WIMPs (weakly interacting big particles) the utilization of gigantic-scale experiments resembling XENON, which is installed underground in a 70,000-gallon tank of water in Italy.
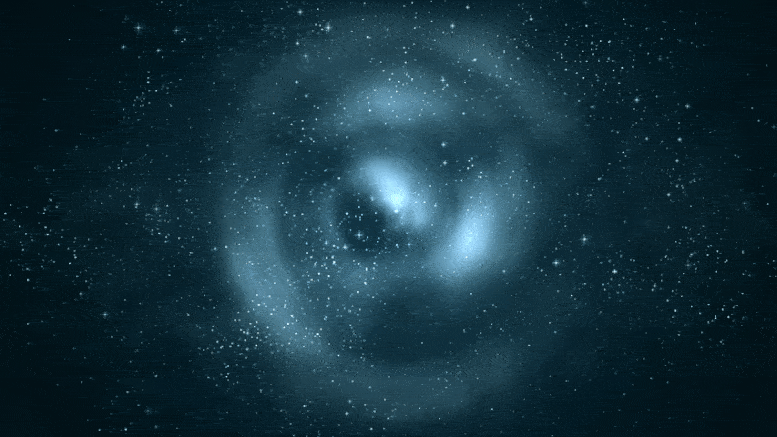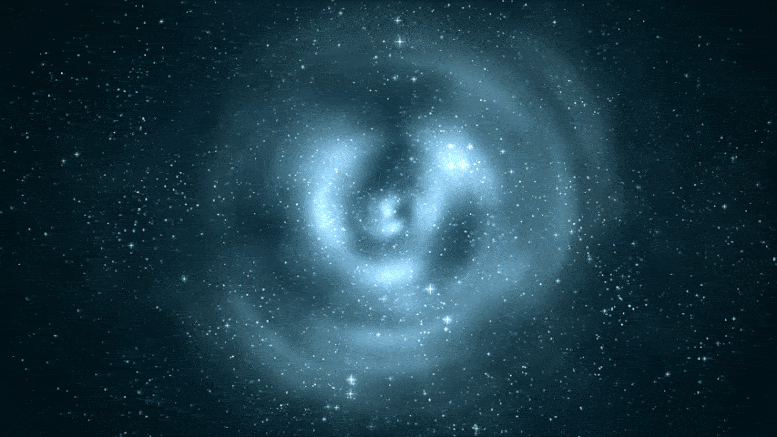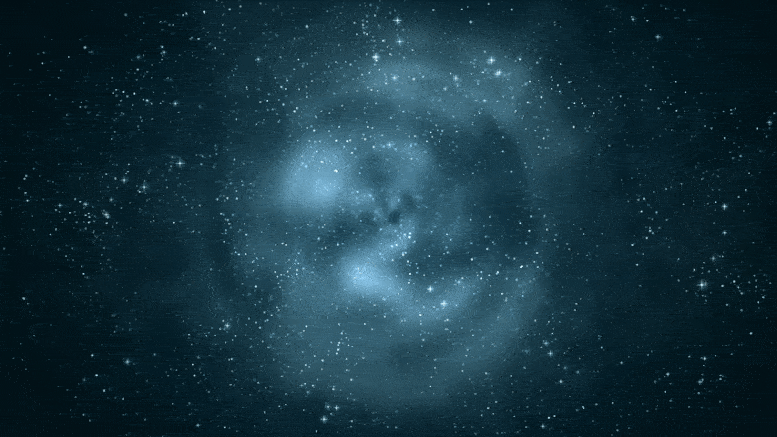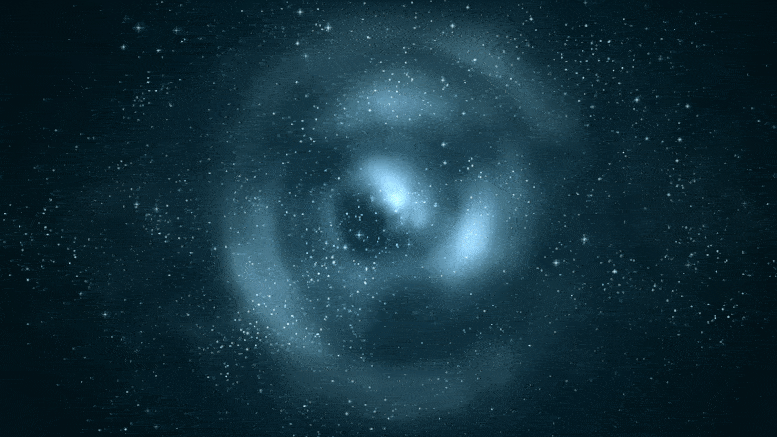
This Hubble Condo telescope composite image shows a ghostly “ring” of shadowy topic in a galaxy cluster. Credit: NASA, ESA, M.J. Jee and H. Ford (Johns Hopkins University)
“Darkish topic is persistently flowing via us, even on this room” says Zurek, who first proposed hidden sector particles over a decade ago. “As we transfer around the heart of the galaxy, this honest wind of shadowy topic largely goes omitted. But we can aloof preserve fair correct thing about that source of shadowy topic, and build fresh systems to observe uncommon interactions between the shadowy topic wind and the detector.”
In a brand fresh paper authorized for e-newsletter in the journal Bodily Overview Letters, the physicists provide an explanation for how the lighter-weight shadowy topic particles could perhaps very wisely be detected via a form of quasiparticle identified as a magnon. A quasiparticle is an emergent phenomenon that occurs when a valuable behaves as if it contains weakly interacting particles. Magnons are a form of quasiparticle by which electron spins—which act admire little magnets—are collectivity furious. In the researchers’ conception for a table-top experiment, a magnetic crystalized field topic could perhaps be passe to observe signs of furious magnons generated by shadowy topic.
“If the shadowy topic particles are lighter than the proton, it turns into very worrying to detect their signal by veteran draw,” says peer author Zhengkang (Kevin) Zhang, a postdoctoral student at Caltech. “But, in accordance to many wisely-motivated fashions, especially these fascinating hidden sectors, the shadowy topic particles can couple to the spins of the electrons, such that once they strike the sphere cloth, they’re going to induce streak excitations, or magnons. If we minimize the background noise by cooling the gear and transferring it underground, we could perhaps hope to detect magnons generated completely by shadowy topic and no longer fashioned topic.”
Such an experiment is totally theoretical at this level nonetheless could perhaps simply eventually happen the utilization of tiny devices housed underground, likely in a mine, where outside influences from varied particles, resembling these in cosmic rays, will also be minimized.
Caltech physicists are designing fresh systems to detect shadowy topic the utilization of magnons, which can perhaps perhaps be quasiparticles that come up when electron spins—which act admire little magnets—are collectivity furious. On this blueprint, a magnetic crystal field topic could perhaps be passe to observe signs of furious magnons generated by shadowy topic. Credit: Caltech/ Zhengkang “Kevin” Zhang
One telltale trace of a uncomfortable topic detection in the table-top experiments could perhaps be changes to the signal that rely on the time of day. That is thanks to the incontrovertible truth that the magnetic crystals that could perhaps be passe to detect the shadowy topic will also be anisotropic, that draw that the atoms are naturally arranged in such one draw that they are inclined to work along with the shadowy topic extra strongly when the shadowy topic comes in from certain directions.
“As Earth moves via the galactic shadowy topic halo, it feels the shadowy topic wind blowing from the direction into which the planet is transferring. A detector fastened at a particular location on Earth rotates with the planet, so the shadowy topic wind hits it from varied directions at varied cases of the day, recount, in most cases from above, in most cases from the facet,” says Zhang. “Throughout the day, as an instance, it is possible you’ll perhaps perhaps perhaps simply maintain the next detection fee when the shadowy topic comes from above than from the facet. Whilst you happen to observed that, it can most likely perhaps perhaps also be moderately spectacular and a undoubtedly strong indication that you had been seeing shadowy topic.”
The researchers maintain varied suggestions about how shadowy topic could perhaps simply impress itself, to boot to via magnons. They’ve proposed that the lighter shadowy topic particles could perhaps very wisely be detected via photons to boot to with but every other type of quasiparticle known as a phonon, which is precipitated by vibrations in a crystal lattice. Preliminary experiments in accordance to photons and phonons are underway at UC Berkeley, where the workforce became once essentially based mostly sooner than Zurek becoming a member of the Caltech college in 2019. The researchers recount that the utilization of these extra than one systems to observe shadowy topic is indispensable because they complement each varied and would attend verify each varied’s outcomes.
“We’re taking a seek for into fresh systems to observe shadowy topic because, given how little we be taught about shadowy topic, it’s value thinking about the whole prospects,” says Zhang.
The peer, titled, “Detecting Light Darkish Topic with Magnons,” became once funded by the Department of Vitality (DOE) and the Nationwide science Foundation (NSF). One other co-author of the peer is Tanner Trickle, a graduate pupil at UC Berkeley.
Reference: “Detecting Light Darkish Topic with Magnons” by Tanner Trickle, Zhengkang Zhang and Kathryn M. Zurek, 15 Might perhaps perhaps also simply 2020, Excessive Vitality Physics – Phenomenology.
arXiv: 1905.13744v2




Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.