(NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space science Institute)
MICHELLE STARR
17 JUN 2019
In its final yr, Cassini plunged where no spacecraft had plunged before, down in the house between Saturn and its rings. Time and again it dove, for a complete of 22 orbits. In the records gathering during these breakneck dives, astronomers admire neutral found new records relating to the system puny moons sculpt and cut these rings.
It is, they are saying, now not easiest new evidence that Saturn’s rings are extra special younger than the planet, however also a window into the system planets originate in the massive rings of grime and debris that circle new child stars.
The new records, tranquil the spend of four of Cassini’s instruments, boom the rings in extra element than ever before.
“It be like turning the vitality up one extra notch on what lets survey in the rings. Each person neutral got a clearer peek of what is going down on,” mentioned Cassini Project Scientist Linda Spilker of JPL-NASA. “Getting that additional dedication answered many questions, however so many tantalising ones remain.”
They boom the comfy straw-like textures and clumps inner the rings, and patterns produced by the motion of the shepherd moons, corresponding to Daphnis. Scientists admire also compiled new maps of the colors, temperatures, and chemistry of the rings.
In flip, this files solutions some fascinating questions. For occasion, a collection of streaks generated by impacts in the F ring – that is the outermost of the main rings – are your complete same length and orientation.
That suggests a flock of impactors that is orbiting Saturn, now not a swarm of rogue cometary debris in orbit in the course of the Solar.
The records also ponied up some new records about Daphnis. The shepherd moon’s shenanigans in its decided lane we name the Keeler gap are already ultimate extra special documented, however new photos admire published skinny strands of ring field topic setting apart from the crests in the moon’s wake.
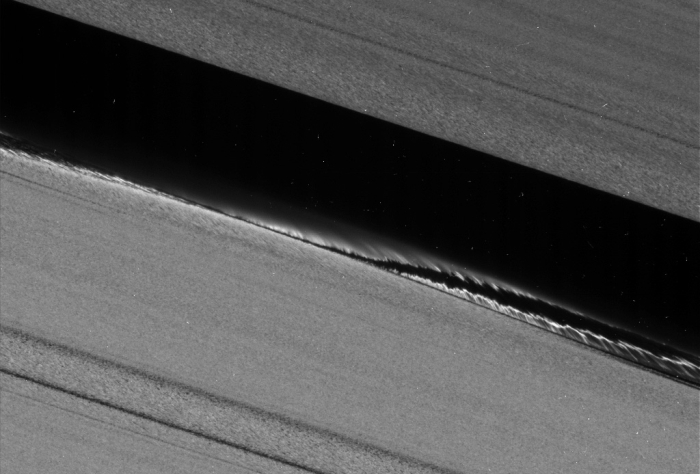 Multiple strands trailing some distance in the lend a hand of Daphnis. (NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space science Institute)
Multiple strands trailing some distance in the lend a hand of Daphnis. (NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space science Institute)
But now not the entirety is enlightening. Cassini scientists spotted something they maintain now not but heed: three obvious textures – refined, clumpy, and streaky. These facets occur in the rings in obvious belts, with sharp, smartly-defined edges.
The topic is, to this point the textures can not be linked to any characteristic of the rings known to this point.
“This tells us the system the rings discover is just not always only a characteristic of how extra special field topic there would possibly be,” mentioned astronomer Matt Tiscareno of the SETI Institute.
“There must be something different relating to the characteristics of the particles, perchance affecting what happens when two ring particles collide and jump off one another.
“And we maintain now not but know what it’s.”
There were extra mysteries in the rings’ chemistry, published by Cassini’s Visible and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer.
In the outermost fragment of the A ring, the spectral draw published an abundance of outdated-authorized water ice. This modified into once a shock, since the characteristic is extremely reflective, which veritably indicates water ice of high purity, or solid water ice. Exactly the plot it’s so reflective is a puzzle.
And the spectral diagnosis also detected no methane or ammonia ice in the rings. Right here is also a head-scratcher, since final yr scientists had found, among other organics, ammonia and methane raining down on Saturn from its innermost ring.
But that is OK. Because, even supposing the probe’s mission ended with regards to two years prior to now now, there would possibly be plenty extra Cassini records but to be unravelled.
“We survey so extra special extra, and nearer up, and we’re getting new and extra spicy puzzles,” mentioned astronomer Jeff Cuzzi of NASA.
“We’re neutral settling into the following phase, which is building new, detailed fashions of ring evolution – alongside side the brand new revelation from Cassini records that the rings are extra special younger than Saturn.”
Better trail even supposing. In 100 million years, these ravishing rings would be entirely long gone.
The research has been printed in Science.




Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.