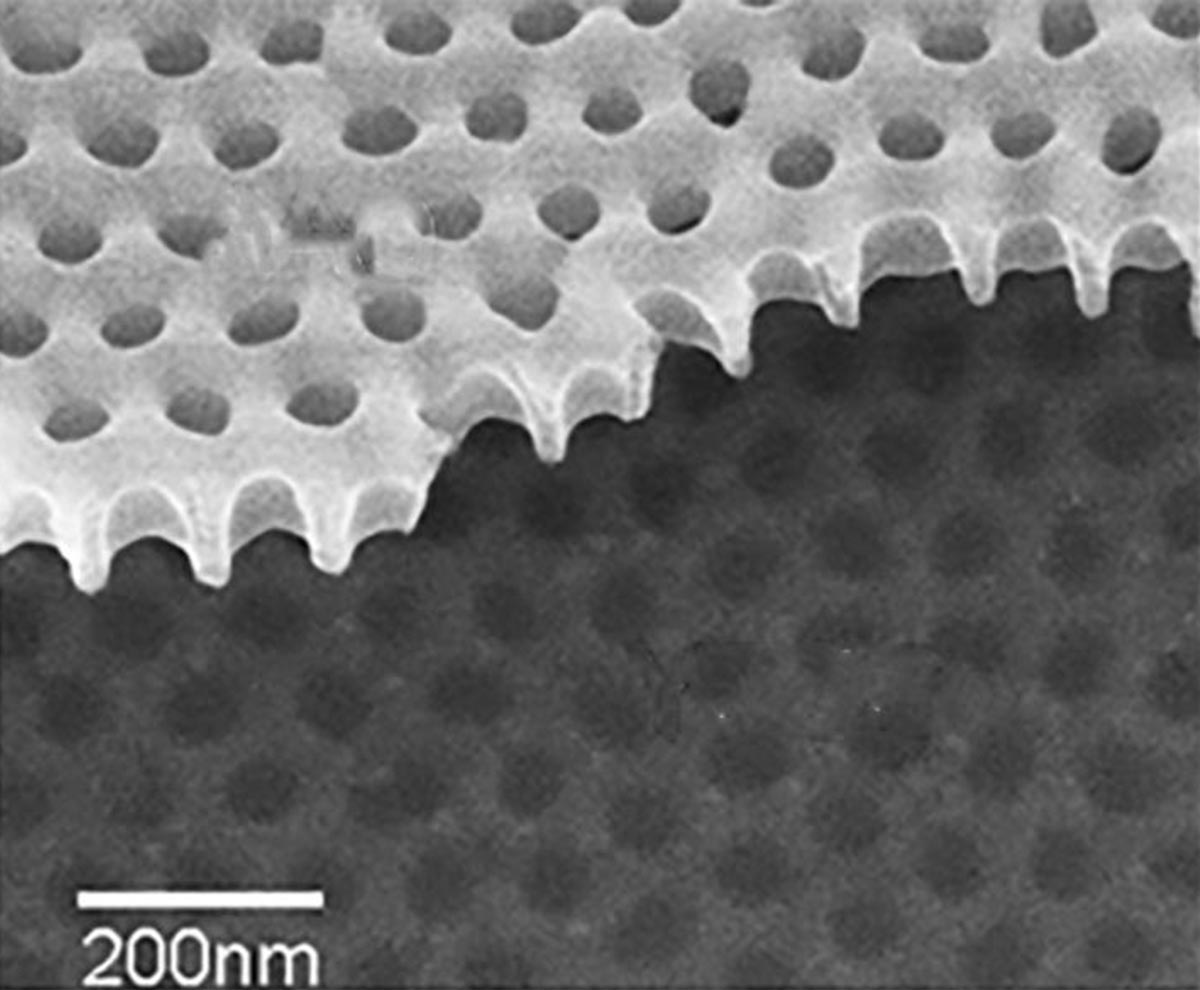
Tiny holes punched into a high-temperature superconducting field materials revealed that Cooper pairs, electron duos that enable superconductivity, can moreover conduct electrical energy the diagram in which metals impact. Credit score: Valles lab / Brown University
In a discovering that finds a totally novel express of matter, study published in the journal science displays that Cooper pairs, electron duos that enable superconductivity, can moreover conduct electrical energy love genuine metals impact.
For years, physicists in discovering assumed that Cooper pairs, the electron duos that enable superconductors to conduct electrical energy with out resistance, were two-trick ponies. The pairs both soar freely, making a superconducting express, or create an insulating express by jamming up internal a field materials, unable to switch at all.
But in a novel paper published on the present time (November 14, 2019) in science, a crew of researchers has shown that Cooper pairs can moreover conduct electrical energy with some quantity of resistance, as current metals impact. The findings record a totally novel express of matter, the researchers express, that can require a novel theoretical explanation.
“There had been proof that this steel express would arise in thin film superconductors as they were cooled down toward their superconducting temperature, but whether or now not or now not that express eager Cooper pairs became an delivery inquire of,” said Jim Valles, a professor of physics at Brown University and the notion’s corresponding creator. “We’ve developed a approach that enables us to test that inquire of and we confirmed that, indeed, Cooper pairs are guilty for transporting charge on this steel express. What’s attention-grabbing is that no-one is extremely obvious at a vital diploma how they impact that, so this discovering will require some more theoretical and experimental work to be aware exactly what’s occurring.”
Cooper pairs are named for Leon Cooper, a physics professor at Brown who gained the Nobel Prize in 1972 for describing their characteristic in enabling superconductivity. Resistance is created when electrons rattle around in the atomic lattice of a field materials as they switch. But when electrons join together to change into Cooper pairs, they undergo a excellent transformation. Electrons by themselves are fermions, particles that obey the Pauli exclusion belief, which diagram every electron tends to abet its absorb quantum express. Cooper pairs, nonetheless, act love bosons, which is in a express to fortunately half the the same express. That bosonic conduct enables Cooper pairs to coordinate their movements with totally different sets of Cooper pairs in a technique the reduces resistance to zero.
In 2007, Valles, working with Brown engineering and physics professor Jimmy Xu, confirmed that Cooper pairs might perhaps perhaps moreover build insulating states to boot to superconductivity. In very thin provides, in preference to shifting in concert, the pairs conspire to take care of in living, stranded on little islands internal a field materials and unable to jump to the subsequent island.
For this novel notion, Valles, Xu, and colleagues in China sought for Cooper pairs in the non-superconducting steel express utilizing a approach akin to the actual person that revealed Cooper pair insulators. The methodology involves patterning a thin-film superconductor — on this case a high-temperature superconductor yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) — with arrays of little holes. When the sphere materials has a most novel working via it and is exposed to a magnetic self-discipline, charge carriers in the sphere materials will orbit the holes love water circling a drain.
“We are able to measure the frequency at which these charges circle,” Valles said. “On this case, we discovered that the frequency is per there being two electrons going around at a time in its set aside aside of perfect one. So we can live that the charge carriers on this express are Cooper pairs and now not single electrons.”
The premise that boson-love Cooper pairs are guilty for this steel express is one thing of a surprise, the researchers express, on story of there are facets of quantum theory that imply this shouldn’t be that chances are high you’ll also take into consideration. So notion perfect what’s going on on this express can also lead to some appealing novel physics, but more study shall be required.
Happily, the researchers express, the truth that this phenomenon became detected in a high-temperature superconductor will get future study more functional. YBCO starts superconducting at around -181 levels Celsius, and the steel half starts at temperatures perfect above that. That’s swish frigid, but it’s vital hotter than totally different superconductors, that are active at perfect above absolute zero. That higher temperature makes it simpler to employ spectroscopy and totally different tactics geared toward higher be aware what’s occurring on this steel half.
Down the avenue, the researchers express, it will also fair be that chances are high you’ll also take into consideration to harness this bosonic metal express for designate novel forms of electronic devices.
“The thing in regards to the bosons is that they’ve got an inclination to be in more of a wavelike express than electrons, so we discuss them having a half and creating interference in vital the the same diagram gentle does,” Valles said. “So there can also fair be novel modalities for shifting charge around in devices by taking half in with interference between bosons.”
But for now, the researchers are delighted to in discovering discovered a novel express of matter.
“science is built on discoveries,” Xu said, “and it’s colossal to in discovering discovered one thing entirely novel.”
###
Reference: “Intermediate bosonic steel express in the superconductor-insulator transition” by Chao Yang, Yi Liu, Yang Wang, Liu Feng, Qianmei He, Jian Solar, Yue Tang, Chunchun Wu, Jie Xiong, Wanli Zhang, Xi Lin, Hong Yao, Haiwen Liu, Gustavo Fernandes, Jimmy Xu, James M. Valles Jr., Jian Wang and Yanrong Li, 14 November 2019, science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.aax5798




Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.