Radio astronomers have detected jets of hot gasoline blasted out by a dusky hole in the galaxy at the heart of the Phoenix galaxy Cluster, positioned 5.9 billion light-years away in the constellation Phoenix. That is a mandatory result for working out the coevolution of galaxies, gasoline, and dusky holes in galaxy clusters.
Galaxies are no longer dispensed randomly in space. Through mutual gravitational enchantment, galaxies assemble together to create collections identified as clusters. The distance between galaxies is no longer entirely empty. There is terribly dilute gasoline all over a cluster which might presumably maybe be detected by X-ray observations.
If this intra-cluster gasoline cooled, it might maybe maybe presumably maybe condense below its have gravity to create stars at the heart of the cluster. Nonetheless, cooled gasoline and stars are no longer veritably seen in the hearts of nearby clusters, indicating that some mechanism wishes to be heating the intra-cluster gasoline and preventing smartly-known particular person formation. One doable candidate for the warmth supply is jets of excessive-tempo gasoline accelerated by a gigantic-big dusky hole in the central galaxy.
The Phoenix Cluster is distinctive in that it does checklist indicators of dense cooled gasoline and big smartly-known particular person formation spherical the central galaxy. This raises the quiz, “does the central galaxy have dusky hole jets as successfully?”
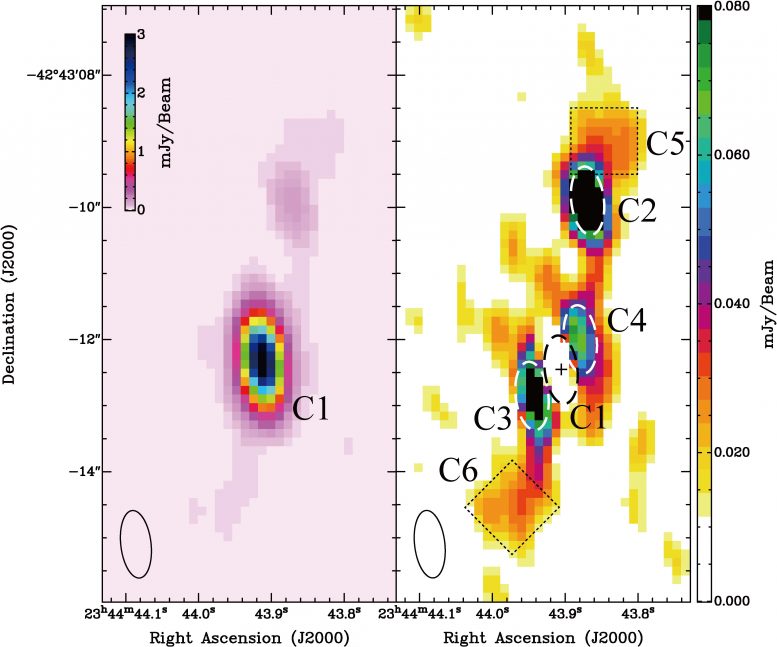
Radio observations of the heart of the Phoenix galaxy Cluster displaying jet structures extending out from the central galaxy. Credit score: Akahori et al.
A team led by Takaya Akahori at the National Gargantuan Observatory of Japan venerable the Australia telescope Compact Array (ATCA) to judge for dusky hole jets in the Phoenix galaxy Cluster with the most attention-grabbing decision to this point. They detected matching structures extending out from reverse sides of the central galaxy. Evaluating with observations of the suppose taken from the Chandra X-ray Observatory archive records shows that the structures detected by ATCA correspond to cavities of much less dense gasoline, indicating that they are a pair of bipolar jets emitted by a dusky hole in the galaxy. Therefore, the team found the first example, in which intra-cluster gasoline cooling and dusky hole jets coexist, in the distant Universe.
Further miniature print of the galaxy and jets might presumably maybe be elucidated by technique of better-decision observations with next generation observational facilities, such because the Sq. Kilometre Array scheduled to originate up observations in the unhurried 2020s.
These results looked as T. Akahori et al. “Discovery of radio jets in the Phoenix galaxy cluster center” in the August 2020 field of Publications of the Gargantuan Society of Japan.
Reference: “Discovery of radio jets in the Phoenix galaxy cluster center” by Takuya Akahori, Tetsu Kitayama, Shutaro Ueda, Takuma Izumi, Kianhong Lee, Ryohei Kawabe, Kotaro Kohno, Masamune Oguri and Motokazu Takizawa, 27 Might presumably maybe 2020, Publications of the Gargantuan Society of Japan.
DOI: 10.1093/pasj/psaa039






Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.