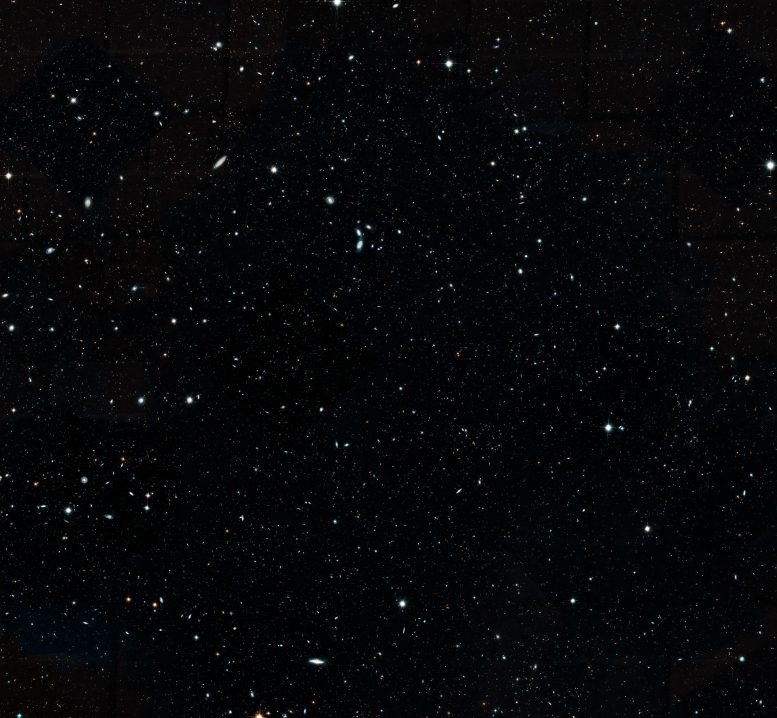

This Hubble Set up aside telescope image represents a share of the Hubble Legacy Field, one in all the widest views of the universe ever made. The image, a combination of thousands of snapshots, represents 16 years’ value of observations. The Hubble Legacy Field contains observations taken by just a few Hubble deep-self-discipline surveys, including the eXtreme Deep Field (XDF), the deepest seek of the universe. The wavelength fluctuate stretches from ultraviolet to come-infrared gentle, capturing the total facets of galaxy meeting over time. This cropped image mosaic items a huge portrait of the some distance-off universe and contains roughly 200,000 galaxies. They stretch assist by 13.3 billion years of time to factual 500 million years after the universe’s birth within the plentiful bang. Credits: NASA, ESA, G. Illingworth and D. Magee (College of California, Santa Cruz), Okay. Whitaker (College of Connecticut), R. Bouwens (Leiden College), P. Oesch (College of Geneva) and the Hubble Legacy Field team
Astronomers earn assign collectively the greatest and most comprehensive “ancient previous e book” of galaxies into one single image, utilizing 16 years’ value of observations from NASA’s Hubble Set up aside telescope.
The deep-sky mosaic, made from nearly 7,500 particular person exposures, provides a huge portrait of the some distance-off universe, containing 265,000 galaxies that stretch assist by 13.3 billion years of time to factual 500 million years after the plentiful bang. The faintest and farthest galaxies are factual one ten-billionth the brightness of what the human watch can think. The universe’s evolutionary ancient previous is also chronicled on this one sweeping seek. The portrait reveals how galaxies switch over time, constructing themselves as a lot as change into the gigantic galaxies considered within the nearby universe.
This ambitious endeavor, known as the Hubble Legacy Field, also combines observations taken by just a few Hubble deep-self-discipline surveys, including the eXtreme Deep Field (XDF), the deepest seek of the universe. The wavelength fluctuate stretches from ultraviolet to come-infrared gentle, capturing the key facets of galaxy meeting over time.
“Now that we now earn long gone wider than in old surveys, we’re harvesting many more some distance-off galaxies within the greatest such dataset ever produced by Hubble,” said Garth Illingworth of the College of California, Santa Cruz, leader of the team that assembled the image. “This one image contains the beefy ancient previous of the growth of galaxies within the universe, from their time as ‘infants’ to after they grew into fully fledged ‘adults.’”
The video begins with a seek of the thousands of galaxies within the Hubble Extremely Deep Field and slowly zooms out to shriek the greater Hubble Legacy Field, containing 265,000 galaxies. Credits: NASA, ESA, G. Illingworth (College of California, Santa Cruz) and G. Sir Francis 1st baron beaverbrook (STScI)
No image will surpass this one until future instruct telescopes are launched. “We’ve assign collectively this mosaic as a instrument to be frail by us and by diversified astronomers,” Illingworth added. “The expectation is that this explore will lead to an draw more coherent, in-depth and elevated working out of the universe’s evolution within the upcoming years.”
The image yields a huge catalog of some distance-off galaxies. “Such pretty high-resolution measurements of the a huge option of galaxies on this catalog allow a huge swath of extragalactic look,” said catalog lead researcher Katherine Whitaker of the College of Connecticut, in Storrs. “Assuredly, these forms of surveys earn yielded unanticipated discoveries which earn had essentially the most appealing affect on our working out of galaxy evolution.”
Galaxies are the “markers of instruct,” as astronomer Edwin Hubble as soon as described them a century ago. Galaxies allow astronomers to stamp the growth of the universe, offer clues to the underlying physics of the cosmos, original when the chemical parts originated, and allow the cases that at remaining ended in the seems to be to be of our describe voltaic machine and life.
This wider seek contains about 30 times as many galaxies as within the old deep fields. The original portrait, a mosaic of a pair of snapshots, covers nearly the width of the beefy Moon. The XDF, which penetrated deeper into instruct than this wider seek, lies on this instruct, nonetheless it indubitably covers decrease than one-tenth of the beefy Moon’s diameter. The Legacy Field also uncovers a zoo of unfamiliar objects. Loads of them are the remnants of galactic “prepare wrecks,” a time within the early universe when small, younger galaxies collided and merged with diversified galaxies.
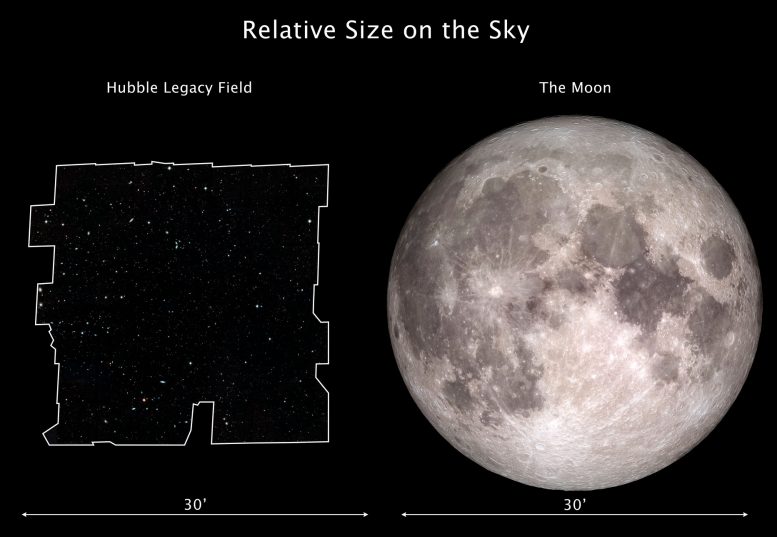
This graphic compares the scale of the Hubble Legacy Field on the sky with the angular size of the Moon. The Hubble Legacy Field is one in all the widest views ever taken of the universe with Hubble. The original portrait, a mosaic of nearly 7,500 exposures, covers nearly the width of the beefy Moon. The Moon and the Legacy Field every subtend about an perspective of 1-half a degree on the sky (or half the width of your forefinger held at arm’s length). Credits: Hubble Legacy Field Characterize: NASA, ESA, and G. Illingworth and D. Magee (College of California, Santa Cruz); Moon Characterize: NASA, Goddard Set up aside Flight Center and Arizona Enlighten College
Assembling all of the observations turned into an mountainous assignment. The image contains the collective work of 31 Hubble applications by diversified teams of astronomers. Hubble has spent more time on this limited instruct than on any diversified instruct of the sky, totaling bigger than 250 days, representing nearly three-quarters of a year.
“Our plot turned into to assemble all 16 years of exposures into a legacy image,” outlined Dan Magee, of the College of California, Santa Cruz, the team’s info processing lead. “Beforehand, these forms of exposures had no longer been assign collectively in a consistent manner that can be frail by any researcher. Astronomers can have interaction the solutions within the Legacy Field they need and work with it straight, slightly than having to perform a huge quantity of data reduction sooner than conducting scientific prognosis.”
The image, along with the particular person exposures that possess up the original seek, is readily accessible to the worldwide mountainous neighborhood by the Mikulski Archive for Set up aside Telescopes (MAST). MAST, a net database of mountainous info from Hubble and diversified NASA missions, is positioned on the Set up aside telescope science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland.
The Hubble Set up aside telescope has approach a lengthy manner in taking ever deeper “core samples” of the some distance-off universe. After Hubble’s birth in 1990, astronomers debated if it turned into value spending a chunk of the telescope’s time to switch on a “fishing expedition” to accumulate a truly lengthy exposure of a small, reputedly blank share of sky. The resulting Hubble Deep Field image in 1995 captured just a few thousand unseen galaxies in one pointing. The plucky effort turned into a landmark demonstration and a defining proof-of-belief that keep of living the stage for future deep self-discipline pictures. In 2002, Hubble’s Developed Camera for Surveys went even deeper to repeat 10,000 galaxies in a single snapshot. Astronomers frail exposures taken by Hubble’s Huge Field Camera 3 (WFC3), installed in 2009, to assemble the eXtreme Deep Field snapshot in 2012. No longer like old Hubble cameras, the telescope’s WFC3 covers a broader wavelength fluctuate, from ultraviolet to come-infrared.
This original image mosaic is the first in a bunch of Hubble Legacy Field pictures. The team is engaged on a second keep of living of pictures, totaling bigger than 5,200 Hubble exposures, in but every other instruct of the sky. In due route, astronomers hope to expand the multiwavelength fluctuate within the legacy pictures to consist of longer-wavelength infrared info and high-energy X-ray observations from two diversified NASA Massive Observatories, the Spitzer Set up aside telescope and Chandra X-ray Observatory.
The plentiful option of galaxies within the Legacy Field image are also prime targets for future telescopes. “This may well increasingly also just the truth is keep of living the stage for NASA’s planned Huge Field Infrared Glance telescope (WFIRST),” Illingworth said. “The Legacy Field is a pathfinder for WFIRST, that can also just earn a image that is 100 times greater than an on a typical foundation Hubble describe. In barely three weeks’ value of observations by WFIRST, astronomers can be ready to assemble a self-discipline that is considerable deeper and bigger than twice as effectively-organized because the Hubble Legacy Field.”
Apart from, NASA’s upcoming James Webb Set up aside telescope will allow astronomers to push considerable deeper into the legacy self-discipline to shriek how the toddler galaxies the truth is grew. Webb’s infrared coverage will dart previous the boundaries of Hubble and Spitzer to assist astronomers name the first galaxies within the universe.
The Hubble Set up aside telescope is a challenge of international cooperation between NASA and ESA (European Set up aside Agency). NASA’s Goddard Set up aside Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Set up aside telescope science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Evaluation in Astronomy in Washington, D.C.





Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.