(CNN)The accidental discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming in 1928, when mould unhealthy one among his petri dishes, changed the direction of neatly-liked medicine, with antibiotics key to the decline of many ailments over the direction of the 20th century.
Now, scientists cling woken up Fleming’s contemporary Penicillium mould and sequenced its genome for the first time. They are saying the certainty they cling got gleaned could maybe well wait on in the battle against antibiotic resistance.
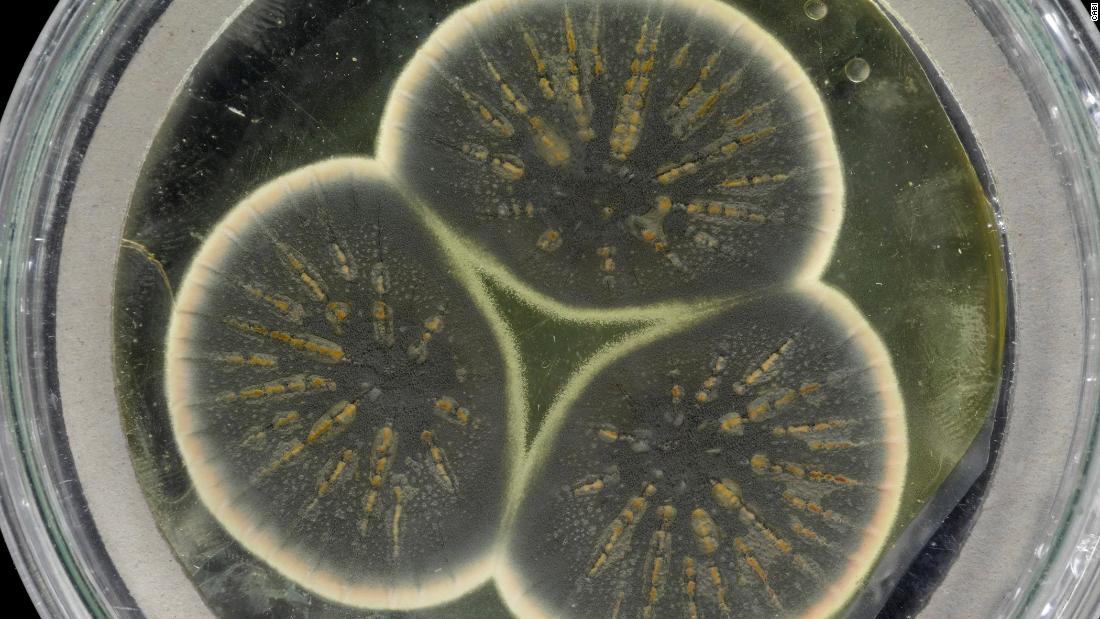
“Remarkably finally this time spent in the freezer, it grows encourage slightly readily. It is miles slightly straightforward, you appropriate fracture it out of that tube and set it on a petri dish plate and away it goes,” said Tim Barraclough, a professor on the Division of Existence Sciences at Imperial College London and the Division of Zoology at Oxford University.
“We realized, to our surprise, that no one had sequenced the genome of this contemporary Penicillium, despite its historical significance to the arena.”
Fleming figured out penicillin in 1928 whereas working at St. Mary’s Hospital Clinical College, which is now section of Imperial College London.
The team regrew Fleming’s contemporary Penicillium from a frozen sample saved on the tradition collection at CABI, which is residence to 30,000 traces of microorganisms, and extracted the DNA for sequencing. The mould had been saved in a freezer there since 1945.
It be now now not the first time the mould has been regrown. In 2019, Penicillium fungus grown from the distinctive stress went on an tutorial world tour to China and India.
Fight against superbugs
The team aged the genetic recordsdata to review Fleming’s mould with two traces of Penicillium from the united states which are aged to construct the antibiotic on an industrial scale.
They checked out two forms of genes: those encoding the enzymes that the fungus uses to construct penicillin; and those who back an eye on the enzymes, as an illustration by controlling what number of enzymes are made. The survey became published Thursday in the journal Scientific Stories.
Barraclough said they were procuring for variations which cling developed naturally over time that could maybe well clarify how antibiotic manufacturing will seemingly be modified to wait on in the battle against superbugs.
“It’ll additionally give us some solutions for how shall we are trying and beef up our utilize or the cling of antibiotics for combating bacteria,” he said.
“A range of effort has been procuring for total new classes of antibiotics. But then when every of those are set into utilize, then the similar factor happens after a duration of time — 5 or 10 years then you have to maybe well presumably cling got purchased resistance to those,” he added.
His team became ” the subtler variations maybe inside of a category of antibiotics and how that could maybe presumably additionally fluctuate in nature and whether we are in a position to utilize those more refined variations to shift the stability somewhat in tackling these bacteria.”
Fleming in the beginning struggled to establish the precise stress of the fungus that created the bacteria-free circle in his petri dish, and over the years, several species of Penicillium were identified as producing penicillin.
At some stage in the 1930s and 1940s, scientists in the UK and US evaluated many various traces to survey if any could maybe well be aged to mass-construct penicillin, and the drug saved hundreds of wounded troopers and civilians all over World War II.
In his lifetime, Fleming realized that his discovery could maybe well be endangered by antibiotic resistance and warned of the dangers at his Nobel lecture in 1945.
“The time could maybe well attain when penicillin will even be sold by someone in the outlets,” he said. “Then there could be the hazard that the ignorant man could maybe well without considerations underdose himself and, by exposing his microbes to nonlethal quantities of the drug, create them resistant.”
Drug resistance is anticipated to consequence in 10 million deaths a year by 2050 as bacteria outsmart our most sophisticated pills.




Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.