MICHELLE STARR
20 OCT 2019
In most up-to-date years, cosmologists peering motivate to the very ruin of day of our Universe comprise found one thing unprecedented. A total bunch of supermassive shaded holes – in a time belief way too early for such big objects to comprise formed.
Precisely how they bought to be so freaking enormous so rapid is a heck of a puzzle – however a new shock discovery would possibly presumably need delivered an solution. The disc of dust and gasoline round a supermassive shaded gap is interesting in this form of formulation that it is slurping down area matter sooner than it would possibly probably presumably in total.
That way it is gaining mass sooner than expected – which in flip would possibly presumably expose what came about within the earliest days of our Universe.
The sphere of this anomalous shaded gap is the coronary heart of a galaxy known as Messier 77, or NGC 1068, round 47 million light-years away.
It’s some distance a Seyfert galaxy, which way the supermassive shaded gap at its centre is actively accreting matter from the location round it.
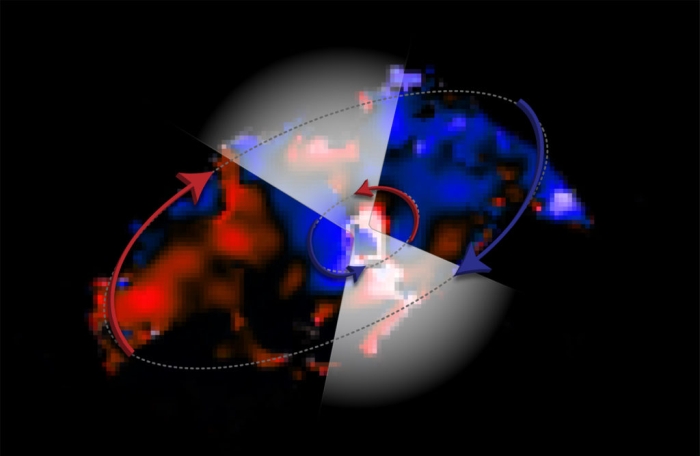
On account of this, the shaded gap is surrounded by an astronomical, swirling, doughnut-formed cloud that, in viewed wavelengths, obscures it and the thin disc of area matter it is slurping up, known as the accretion disc. But must you gawk on the shaded gap in radio wavelengths, the next level of ingredient might perchance presumably also be picked out.
That’s what a group of astronomers simply did, the exhaust of the Atacama Big Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile.
Thanks to this new stare, they comprise been able to measure the motion of the gasoline within the internal orbits of the torus – and so that they came across one thing surprising.
 (ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), V. Impellizzeri; NRAO/AUI/NSF, S. Dagnello)
(ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), V. Impellizzeri; NRAO/AUI/NSF, S. Dagnello)
“Surprisingly, we found two discs of gasoline rotating in opposite directions,” said astronomer Violette Impellizzeri of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO).
“Counter-rotating gasoline streams are unstable, which way that clouds descend into the shaded gap sooner than they finish in a disk with a single rotation route. This would possibly presumably also be a formulation wherein a shaded gap can grow rapid.”
The supermassive shaded gap on the coronary heart of M77 – aka M77* – is round 15 million occasions the mass of the Solar, which way its match horizon is over 88 million kilometres (54 million miles) across. But its gravitational affect extends mighty farther.
In line with the group’s observation, the internal disc swirling across the shaded gap (and into it, like water into a drain) begins at about 2 light-years from the shaded gap, and extends to about 4 light-years. That is rotating one way.
The torus itself extends mighty farther, from 4 light-years to 22 light-years. It’s rotating within the change route.
If here is certainly how shaded holes grow more rapid, it is in actual fact wintry. But! It’s moreover raised one other enormous mystery.
“We did no longer ask to gawk this, because gasoline falling into a shaded gap would in total budge round it in easiest one route,” Impellizzeri said. “One thing will deserve to comprise apprehensive the drift, since it is no longer doubtless for a section of the disc to originate rotating backward all on its non-public.”
Counter-rotational flows in situation are no longer in actual fact unprecedented. The article is, even though, is that they’re customarily viewed on plenty of scales – galactic scales, where the counter-rotation occurs hundreds of light-years away from the galactic centre.
“The counter-rotation constantly outcomes from the collision or interaction between two galaxies,” said astronomer Jack Gallimore from Bucknell College.
“What makes this end result excellent is that we watch it on a mighty smaller scale, tens of light-years in preference to hundreds from the central shaded gap.”
What the group thinks would possibly presumably need came about is that counter-rotating area matter fell into the torus from the host galaxy, or a passing counter-rotating satellite tv for pc dwarf galaxy bought sucked in. And, even though the orbits are at this time stable, the pains is doubtless a quick one.
“[It] will alternate when the outer disc begins to descend onto the internal disc, which would possibly presumably occur after about a orbits or about a hundred thousand years. The rotating streams of gasoline will collide and change into unstable, and the disks will doubtless collapse in a vivid match as the molecular gasoline falls into the shaded gap,” Gallimore said.
“Unfortunately, we is per chance no longer there to verify the fireworks.”
Bummer.
The learn has been printed in The Astrophysical Journal.





Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.