The annotated living of Mars on this illustration holds arrive-ground water ice that would possibly maybe be with out be anxious accessible for astronauts to dig up. The water ice modified into identified as fragment of a map utilizing info from NASA orbiters. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA has mountainous plans for returning astronauts to the Moon in 2024, a stepping stone on the lag to sending humans to Mars. However the attach would possibly maybe light the important other folks on the Purple Planet land?
A new paper published in Geophysical Be taught Letters would possibly maybe aid by offering a map of water ice believed to be as tiny as an glide (2.5 centimeters) under the bottom.
Water ice is known as a key consideration for any seemingly touchdown set. With tiny room to spare aboard a spacecraft, any human missions to Mars can grasp to harvest what’s already available for drinking water and making rocket fuel.
NASA calls this thought “in situ handy resource utilization,” and it’s a needed part in selecting human touchdown websites on Mars. Satellites orbiting Mars are needed in serving to scientists determine the ideal places for building the important Martian study living. The authors of the brand new paper assemble use of information from two of these spacecraft, NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and Mars Odyssey orbiter, to stumble on water ice that would potentially be nearby of astronauts on the Purple Planet.
“You wouldn’t need a backhoe to dig up this ice. That you might most definitely use a shovel,” said the paper’s lead author, Sylvain Piqueux of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. “We’re persevering with to assemble info on buried ice on Mars, zeroing in on the ideal places for astronauts to land.”
Buried Treasure on Mars
Liquid water can’t closing in the skinny air of Mars; with so tiny air stress, it evaporates from a solid to a gas when uncovered to the ambiance.
Martian water ice is locked away underground all the blueprint in which via the planet’s mid-latitudes. These areas arrive the poles grasp been studied by NASA’s Phoenix lander, which scraped up ice, and MRO, which has taken many photos from living of meteor impacts which grasp excavated this ice. To search out ice that astronauts would possibly maybe with out be anxious dig up, the mediate about’s authors relied on two warmth-gentle devices: MRO’s Mars Local weather Sounder and the Thermal Emission Imaging Machine (THEMIS) digicam on Mars Odyssey.
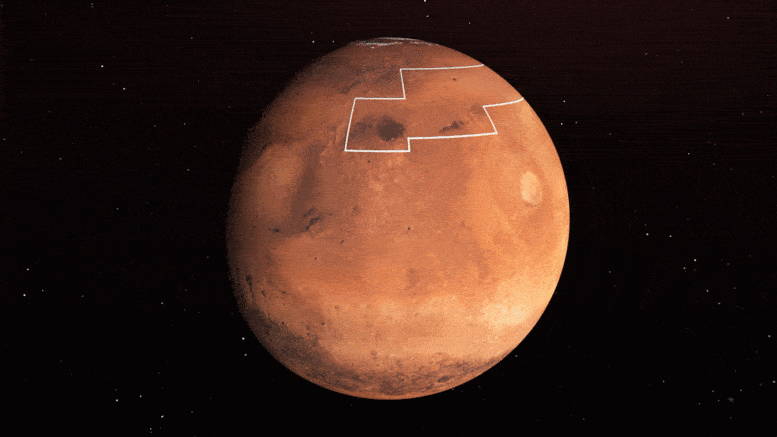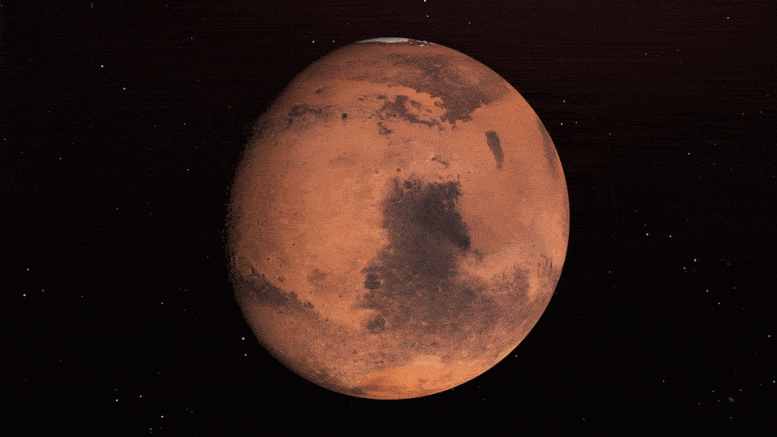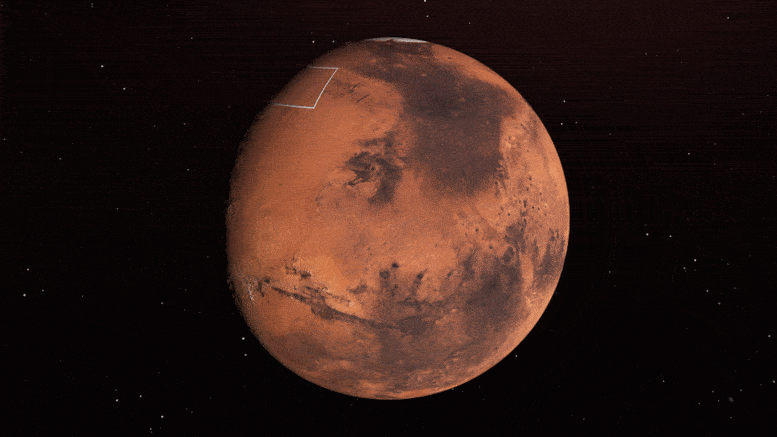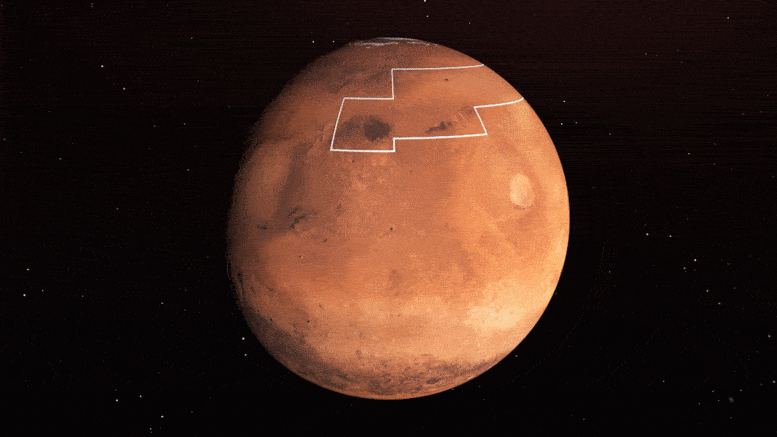
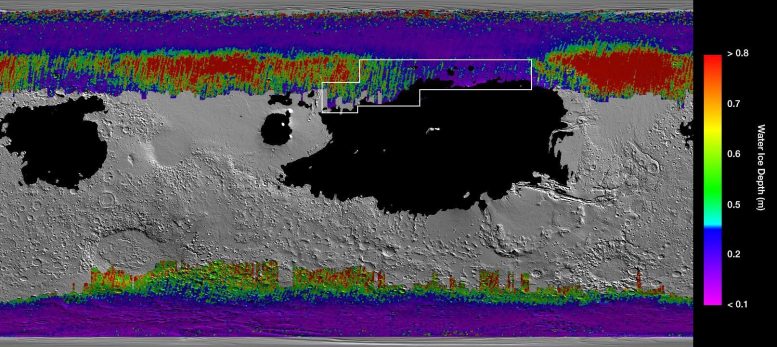
This rainbow-colored map presentations underground water ice on Mars. Frosty colours are nearer to the bottom than warm colours; shaded zones display areas the attach a spacecraft would sink into dazzling dust; the outlined field represents the correct space to send astronauts for them to dig up water ice. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU
Why use warmth-gentle devices when procuring for ice? Buried water ice adjustments the temperature of the Martian ground. The mediate about’s authors coarse-referenced temperatures suggestive of ice with other info, such as reservoirs of ice detected by radar or seen after meteor impacts. Recordsdata from Odyssey’s Gamma Ray Spectrometer, which is tailored for mapping water ice deposits, were also precious.
As expected, all these info imply a trove of water ice all the blueprint in which via the Martian poles and mid-latitudes. However the map unearths namely shallow deposits that future mission planners would possibly maybe are seeking to mediate about further.
Deciding on a Touchdown Space
Whereas there are hundreds places on Mars scientists would admire to hunt the recommendation of with, few would assemble realistic touchdown websites for astronauts. Most scientists grasp homed in on the northern and southern mid-latitudes, which grasp extra critical sunlight and warmer temperatures than the poles. But there’s a heavy need for touchdown in the northern hemisphere, which is steadily decrease in elevation and provides extra ambiance to slack a touchdown spacecraft.
A gigantic a part of a neighborhood called Arcadia Planitia is the most tempting purpose in the northern hemisphere. The map presentations hundreds blue and red on this space, representing water ice lower than one foot (30 centimeters) under the bottom; warm colours are over two toes (60 centimeters) deep. Sprawling shaded zones on the map teach areas the attach a touchdown spacecraft would sink into dazzling dust.
What’s Subsequent?
Piqueux is planning a total campaign to proceed discovering out buried ice across assorted seasons, watching how the abundance of this convenient resource adjustments over time.
The extra we glance arrive-ground ice, the extra we gather,” said MRO Deputy Challenge scientist Leslie Tamppari of JPL. “Staring at Mars with extra than one spacecraft over the route of years continues to provide us with new solutions of discovering this ice.”
###
Reference: “Frequent Shallow Water Ice on Mars at Excessive and Mid Latitudes” by Sylvain Piqueux, Jennifer Buz, Christopher S. Edwards, Joshua L. Bandfield, Armin Kleinböhl, David M. Kass and Paul O. Hayne, 10 December 2019, Geophysical Be taught Letters.
DOI: 10.1029/2019GL083947
JPL manages the MRO and Mars Odyssey missions for NASA’s science Mission Directorate in Washington. Lockheed Martin Dwelling in Denver built each orbiters. JPL built and operates the Mars Local weather Sounder instrument. THEMIS modified into built and is operated by Arizona State University in Tempe. The Gamma Ray Spectrometer modified into built and is operated by the University of Arizona in Tucson.




Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.