(NASA/IBEX/Adler Planetarium)
NASA astronomers be pleased ragged knowledge from the Voyager probes to measure the bustle of particles rippling at the very edge of our Solar System, and chanced on the tension within the some distance away borderlands of our huge title is increased than they expected.
The outcomes suggest “that there are another parts to the tension that are usually now not being belief of as correct now that would possibly maybe presumably contribute,” says Princeton University astrophysicist Jamie Rankin.
Perchance there are whole populations of particles within the market that have not been taken into story yet. Or even it is ideal just a dinky hotter than anybody figured. The researchers be pleased hundreds of in all probability explanations to explore in future learn.
While the discovery itself is interesting sufficient, it is the manner they realized it that makes for a in actuality racy bit of science.
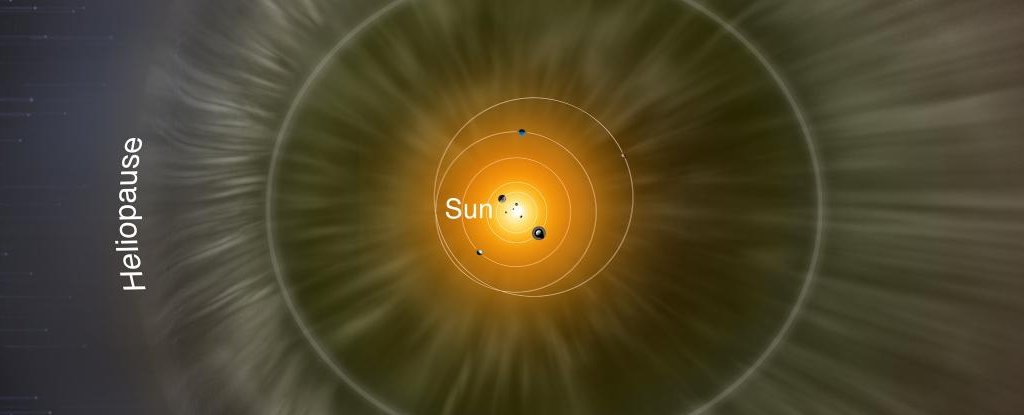
As plasma within the form of solar wind emanates from our Solar, it kinds a ‘bubble’ we call the heliosphere. Fourteen billion kilometres some distance off from the huge title, that wind successfully runs out of steam, as charged particles all of sudden unhurried to subsonic speeds.
The brink of this bubble, called the heliosheath, is a zone the put the density of those charged particles drops off and magnetic fields develop dilapidated.
Previous this messy border is a skinny shell called the heliopause, the put the haze of plasma blown out by the Solar trickles away, nudged by the shapely impact of our galactic neighbours as our huge title moves through space.
At this ‘discontinuance’, the tension of local interstellar space pushing in and the heliosheath pushing out must steadiness out. Radiant precisely what this appears like, even supposing, is not any easy job. We can fabricate fashions to estimate, however nothing beats though-provoking evidence.
Fortunately, we happen to be pleased two probes passing through that portion of the Solar System. Desire a peek at NASA’s to hand draw under to peek how it all suits collectively.
 (NASA’s Goddard Home Flight Heart/Mary Pat Hrybyk-Keith)
(NASA’s Goddard Home Flight Heart/Mary Pat Hrybyk-Keith)
Voyager 1 is set 20 billion kilometres away, successfully out within the wild emptiness we agree with of as interstellar space. Its accomplice, Voyager 2, is now not some distance within the relief of, correct on the cusp of making an exit.
Neither has a say manner of telling us worthy referring to the pressures of space in that space, however a contemporary flare-up in solar job called a international merged interplay space (GMIR) equipped a high different to work it out.
“There become in actuality appealing timing for this match because we seen it correct after Voyager 1 crossed into the local interstellar space,” says Rankin.
“And whereas this is the principle match that Voyager seen, there are extra within the tips that we can proceed to peek at to peek how things within the heliosheath and interstellar space are changing over time.”
The solar job become successfully a weep into space, sending a pulse of particles roaring out into the gap. This weep rippled into the heliosheath in 2012, the put Voyager 2 become looking at and listening. Roughly three months later, Voyager 1 additionally felt its outcomes.
From each and every location of observations, the researchers calculated the tension at the boundary to be around 267 femtopascals, which is a actually minuscule portion of the roughly atmospheric tension we skills right here on Earth.
It goes to be a comparatively small squeeze, however the researchers were taken aback.
“In at the side of up the pieces identified from outdated learn, we realized our original price is quiet bigger than what’s been measured so some distance,” says Rankin.
The team were additionally in a space to calculate the velocity of sound waves passing through this medium – a rapid 314 kilometres per second. Or a thousand cases faster than sound travelling through our be pleased ambiance.
There become one other surprise to come. The wave’s passage lined up with an obvious fall within the depth of high bustle particles called cosmic rays. The truth each and every of the probes experienced this identical thing in two assorted suggestions affords astrophysicists yet one other mystery to resolve.
“Looking out for to note why the trade within the cosmic rays is assorted within and outdoors of the heliosheath stays an open question,” says Rankin.
The Voyager probes would be getting just a dinky dilapidated, however given how busy it appears out on the brink of the Solar System, we’re chuffed they have not completely retired yet.
This learn become published in The Astrophysical Journal.




Leave a comment
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.